TL;DR
- MongoDB Atlas is a managed, multi‑cloud platform that runs the MongoDB document database and adds integrated services like full‑text search, vector search and stream processing.
- The release of MongoDB 8.0 (October 2024) delivers 36 % faster reads, 59 % higher update throughput and introduces range queries on encrypted data.
- New features for AI and search include Atlas Vector Search with vector quantization and dedicated search nodes, reducing query latency by 40–60 %.
- Cost‑optimization updates announced in 2024 allow independent shard scaling, extended storage and more responsive auto‑scaling.
- Pricing tiers range from a free M0 cluster (512 MB storage) to dedicated clusters starting at $0.08/hr. The Flex tier costs $8–$30 per month depending on operations per second.
- To get started, create an Atlas account, deploy a cluster, whitelist your IP, create a database user and connect using your preferred client. Load sample data and explore with Data Explorer or MongoDB Compass.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- MongoDB Atlas
- Getting Started with MongoDB Atlas
- Summary
- Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Question
- What is MongoDB Atlas?
- Is there a free version of MongoDB Atlas?
- What are the main pricing options?
- What’s new in MongoDB 8.0?
- How does Atlas support AI and vector search?
- How does Atlas manage scaling and cost optimization?
- Does Atlas provide tools for data visualization?
- Can I deploy Atlas in multiple regions?
Since you’re interested in MongoDB Atlas, here are a couple of quick Mongo resources. If you have a project and are trying to find a BI solution for your Mongo data, take a look at our MongoDB Analytics page where you can start a Knowi trial. You can also set up a 15-minute call with a member of our team to see if Knowi may be a good BI solution for your project.
In the last decade the database industry has moved decisively toward database‑as‑a‑service (DBaaS). Rather than managing on‑premises servers, many organizations now rely on cloud platforms that handle hardware provisioning, patching and backups. At the same time the types of data stored have changed: businesses increasingly need to work with semi‑structured or unstructured data, develop AI‑enabled applications and scale workloads dynamically. These requirements have helped spur adoption of NoSQL databases and event‑driven services. MongoDB, best known for its document‑oriented database, launched MongoDB Atlas to deliver the advantages of a managed database platform across AWS, Azure and Google Cloud.
This article provides an up‑to‑date overview of MongoDB Atlas, including new features released in late 2024 and early 2025, current pricing tiers and a practical getting‑started guide.
Introduction
Database-as-a-Service
In recent years, the database industry has undergone a number of changes, resulting in an increased shift towards a database as a service (DBaas) model versus an on-premise infrastructure. Databases are at the core of most business apps, and cloud-based DBaaS services offers users a flexible, scalable, and on-demand platform that eliminates the need to set up costly physical hardware, install software, or configure for performance. In addition, the data companies are analyzing is also changing. Users and developers now look for more adaptable databases that allow them to access and work with unstructured data. Along with this has come a greater demand for in-memory and NoSQL databases with a pay-per-use model.
MongoDB, the company behind the open source database, sought to fill this need with Atlas, its own DBaaS offering that provides users with a managed database service. The service offers pay-as-you go pricing and allows users to deploy on the cloud service provider of their choice (AWS, Azure, and GCP). Atlas has been a success for MongoDB, and as of 2019 accounts for 35% of its total revenue with over 12,000 customers.
DBaaS offerings let teams spin up a fully managed database in minutes and scale up or down on demand. Rather than purchasing servers and tuning databases manually, users provision a service through a web console or API. The provider handles infrastructure provisioning, patching, backups and redundancy. DBaaS also makes it easy to try out different providers or move between regions. MongoDB Atlas is one of several DBaaS solutions; others include Amazon DocumentDB and Azure Cosmos DB.
In this post, we’ll provide an overview of MongoDB Atlas, give a tutorial on getting started with the platform, and share our general takeaways from a first-time user perspective.
MongoDB Atlas
Overview
MongoDB Atlas is a cloud-based, open-source, NoSQL database that uses JSON documents with dynamic schemas, serving as an alternative to table databases. Atlas provides all the features of MongoDB, while automating database administration tasks such as database configuration, infrastructure provisioning, patches, scaling events, backups, and more, freeing up developers to focus on what matters to them most.
MongoDB Atlas also provides the dual benefit of flexibility and scalability. Dynamic schemas allow users to change the schema of their data without modifying it, providing flexibility. While its “automatic sharding” feature allows users to scale up or out across a range of instances, with zero application downtime.
Key capabilities include:
- Managed document database: Atlas handles configuration, provisioning, patching, backups and scaling. Users work with the same MongoDB API but don’t need to administer the underlying infrastructure.
- Flexibility & scalability: Dynamic schemas allow data models to evolve without downtime. Automatic sharding distributes data across nodes to support horizontal scaling.
- Multi‑cloud deployment: Clusters can run on AWS, Azure or Google Cloud. You can deploy multi‑region clusters for low‑latency global access.
- Integrated services: Atlas includes features such as full‑text search, vector search (for generative‑AI applications), stream processing and data federation. Atlas Vector Search added vector quantization in 2024, allowing customers to scale to billions of vectors at lower cost. Dedicated search nodes were also introduced; by providing specialized infrastructure for search and vector workloads they cut query latency by roughly 40-60% and are generally available on AWS, Google Cloud and Azure
- AI‑ready platform: MongoDB 8.0 (released October 2024) features architectural optimizations that deliver 36 % faster reads and 59 % higher update throughput. It also adds range queries in Queryable Encryption, enabling queries on encrypted data. The MongoDB AI Applications Program (MAAP) launched in 2024 and provides customers with AI specialists, partner integrations and best practices to accelerate AI projects.
- Cost‑optimization tools: In late 2024 MongoDB announced enhancements such as independent shard scaling, extended storage on Azure (supporting clusters with more than 4 TB of storage) and up‑to‑5× faster auto‑scaling. These features let teams scale shards, storage and compute separately, which helps avoid over‑provisioning and reduces costs.
Pricing
Free Tier
MongoDB offers a free tier that users can use for learning, prototyping, and early deployment. This free edition called M0 Sandbox is limited to 512MB of storage, shared vCPU and RAM, 100 max connections, and a limit of one M0 cluster.
Paid Tiers
MongoDB Atlas offers several pricing tiers, all billed hourly with monthly invoices. Prices vary by cloud region and usage, so the figures below should be treated as general guidance.
Free Tier (M0)
- Cost: Free forever.
- Resources: 512 MB storage with shared RAM and shared vCPU.
- Use case: Learning, prototyping and small applications. Note that the free tier is limited to one cluster.
Dedicated Clusters
Dedicated clusters are suited for production workloads. Pricing depends on the instance size and cloud provider:
- Base price: Starts at $0.08 per hour for an M10 cluster (10 GB storage, 2 GB RAM and 2 vCPUs). Larger instances provide more storage and compute; for example, an M40 (80 GB storage, 16 GB RAM and 4 vCPUs) costs around $1.04 per hour.
- Scale: Dedicated clusters can range from 10 GB to 4 TB of storage and 2 GB to 768 GB of RAM.
- Cost optimization: Features like auto‑scaling, independent shard scaling and extended storage help manage costs by matching resources to workload demand.
Flex Tier
The Flex tier provides predictable pricing with a monthly cap, making it ideal for development and variable workloads. Key details include:
- Base fee: Costs $8 per month for workloads up to 100 operations per second.
- Scaling: As usage increases, the marginal monthly cost decreases. For example, 100–200 ops/sec costs $7 more (total $15/mo), 200–300 ops/sec adds $6 more (total $21/mo), and so on up to a cap of $30 per month for 400–500 ops/sec.
- Hourly billing: Approximately $0.011/hour for the base tier.
Serverless Pricing
Serverless clusters bill only for operations run. Typical charges include:
- Read Processing Units (RPUs): About $0.10 per million read operations for the first 50 million per day, with discounted tiers at higher usage.
- Write Processing Units (WPUs): $1.00 per million writes.
- Storage: $0.25 per GB‑month.
- Backups & data transfer: Basic daily snapshots are free; additional backups and cross‑region data transfer incur small fees.
Tip: Pricing can vary by region and provider. For the latest rates and volume discounts, consult the official MongoDB Atlas pricing page or use the cost calculators provided in the console.
Getting Started with MongoDB Atlas
MongoDB Atlas makes it easy to get started and registering for the free tier takes only seconds. The whole process uses a dynamic web interface that walks you through various deployment options. It’s easy, intuitive and doesn’t require specialized knowledge. Below, we’ll go through the steps of getting up and running with MongoDB Atlas.
Creating an Atlas Account
First, you’ll need to register for an account on the MongoDB Atlas landing page. The registration form only needs you to provide basic information like name, email, company and for you to create a password. No credit card info is required. Once you register, Atlas automatically creates a default organization and project where you can deploy your first cluster.

Deploy a Free Tier Cluster
After logging in, you’ll be prompted to build your first cluster by choosing a cloud provider and region. Atlas works with the three primary cloud providers Amazon AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure. Based on your choice, you can pick the location of the preferred data center location. Free tiers and regions are flagged for the free sandbox version and creating a new cluster took only a few minutes.
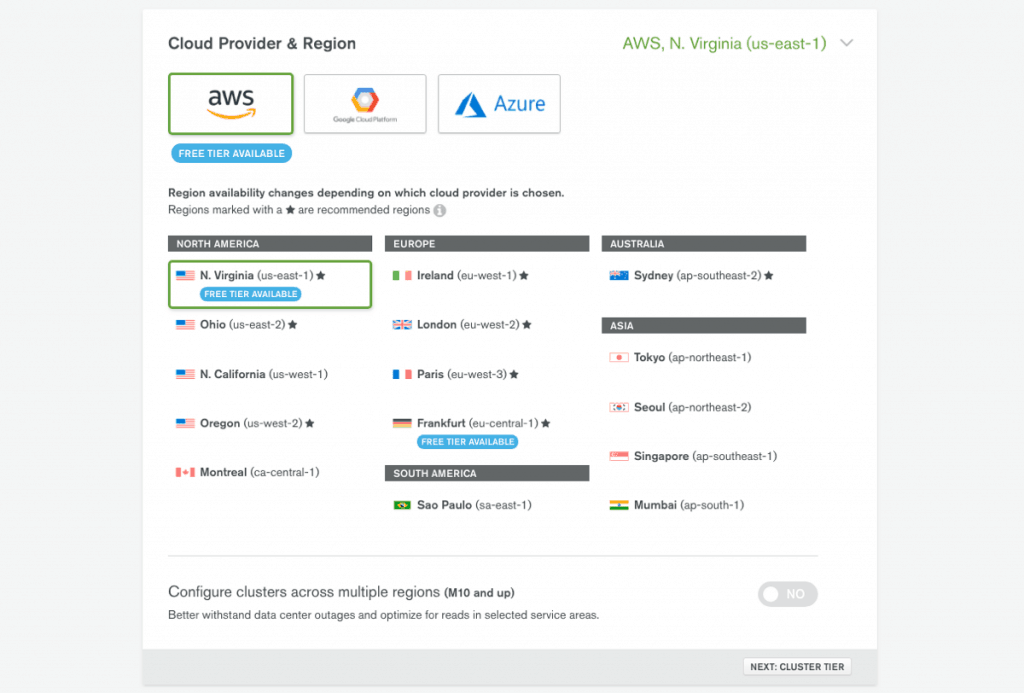
Whitelist Your Connection IP Address
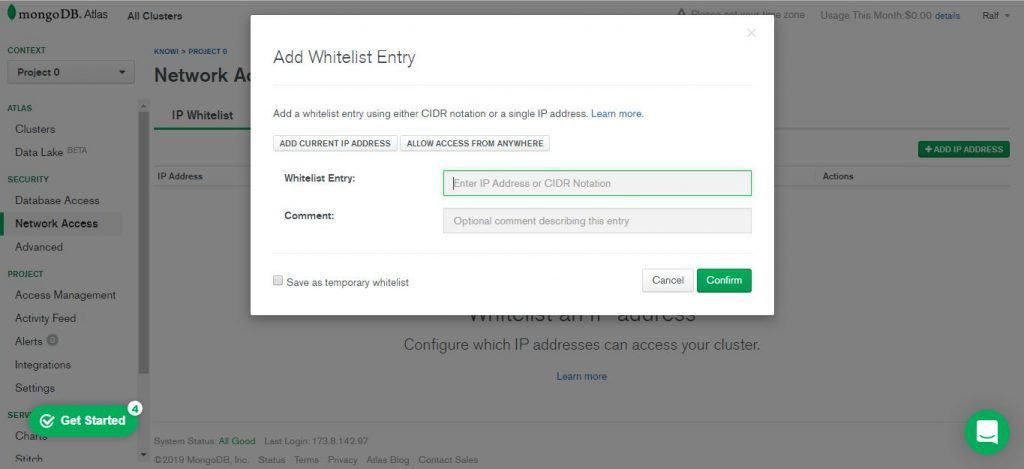
You will then be prompted to set up your Internet Protocol (IP) and whitelist your IP address. This is important, as it ensures that only you can access the cluster in the cloud from your IP address. You also have the option of allowing access from anywhere, though this means that anyone can have network access to your cluster. This is a potential security risk if your password and other credentials leak.
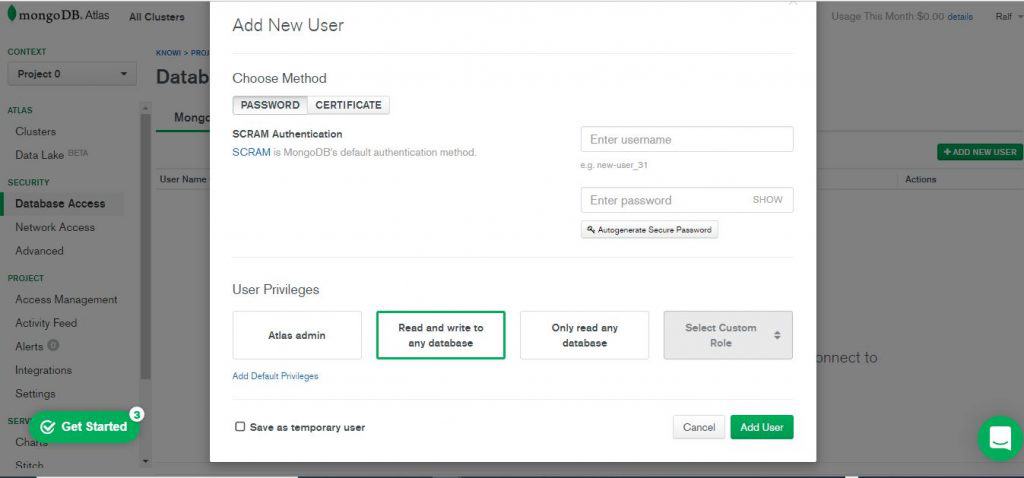
Create a MongoDB User for Your Cluster
Next, you’ll need to create a MongoDB user to access your cluster. Simply enter the new username and password. You’ll then have the option of selecting user privileges, including admin, read/write access, or read-only access.
Connect to Your Cluster
Now that you’ve created a user, it’s time to connect to your cluster. You’ll be prompted to select a connection method, either connecting with MongoShell, your own application, or MongoDB Compass, MongoDB’s GUI. In this example, we’ll connect using MongoDB Compass.
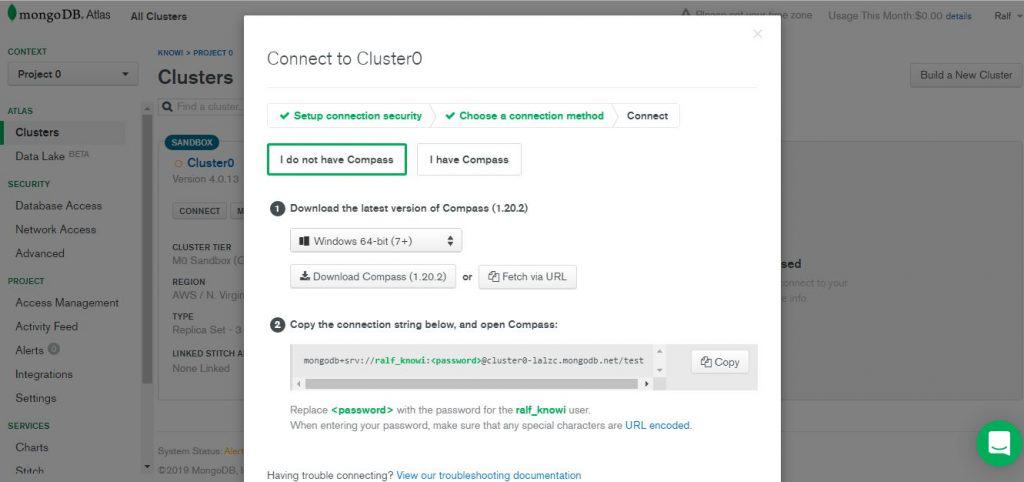
Once you’ve downloaded and opened MongoDB Compass, you’ll be prompted to paste a connection string from your clipboard, then connect to your cluster.
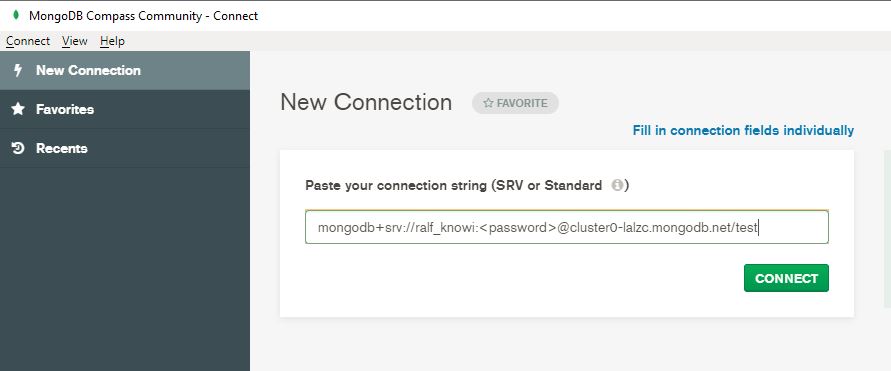
Insert and View Data in Your Cluster
Now that you’re connected to your cluster, you can now insert and interact with sample data on your cluster using Data Explorer.
Data Explorer allows you to view, create, and drop databases, collections, and indexes in your cluster. In addition, you can insert, edit, and delete documents, as well as create and run aggregation pipelines to process your data. Note that Data Explorer is a feature within Atlas that allows you to access and manage data inside your clusters, different from MongoDB Compass, a stand-alone GUI used to interact with MongoDB databases (we’ll discuss this further in Part 2 of this post).
First, you’ll need to load the sample data set into your cluster. Once loaded, you can access it in Data Explorer by clicking the Collections button (or with Mongo Shell). The data import takes approximately 5 mins and once the operation finishes, you will see five databases in your cluster:
- sample_airbnb
- sample_geospatial
- sample_mflix
- sample_training
- Sample_weatherdata
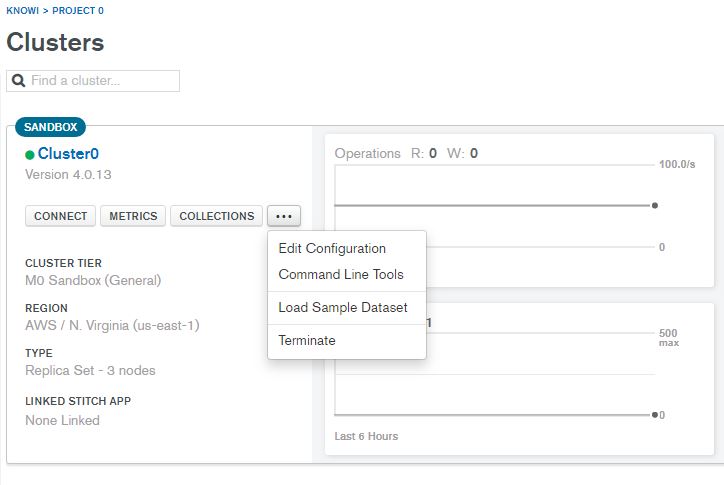
Now that you have imported data into your cluster, you can now view and modify them. You can also use Data Explorer’s Filter bar to search for specific documents, edit documents (i.e. add fields), then save your updates.
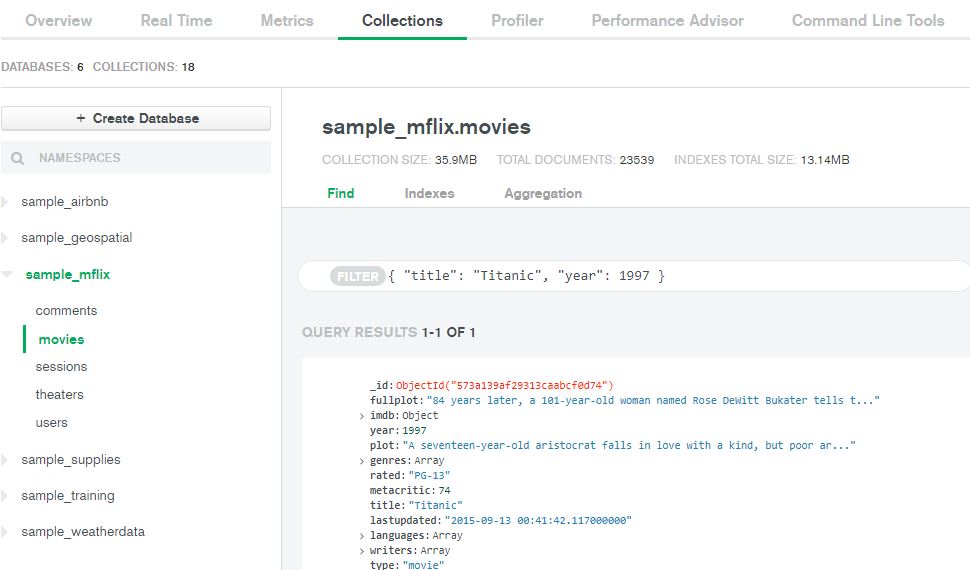
And just like that, we have gone through the entire process of registering for an Atlas account, deployed and connected to your first Atlas cluster, populated your cluster with sample data, and interacted with the data using Atlas Data Explorer. As you can see, getting started with Atlas was delightfully simple and straightforward.
Summary
Overall, we found MongoDB Atlas to be easy to use and get acclimated to. The process of registering for an account, deploying your first cluster, and connecting to your cluster was seamless thanks in large part to its intuitive interface. In particular, we liked that Atlas included sample data that we were able to load into our cluster and then utilize the Data Explorer GUI to interact with the data.
Its simple user interface, along with its host of features including scalability with automatic sharding, built-in automation mechanisms for operational tasks, and excellent performance that provides high throughput and low latency even for the most demanding workloads, and it’s no wonder that experienced developers and new users alike have grown to love MongoDB Atlas.
In Part 2 of this post, we’ll continue where we left off and delve deeper into visualization solutions for your MongDB data including Mongo’s GUI tools like MongoDB Compass, industry standard BI tools, and native solutions like MongoDB Charts – Mongo’s own charting tool that allows you to create visual representations of your MongoDB data stored in MongoDB Atlas. We will also be introducing Knowi for MongoDB analytics. Knowi is an analytics platform purpose-built for modern data stacks for more advanced data analytics and visualization.
Takeaways
MongoDB Atlas has evolved from a managed document database to a comprehensive developer data platform. Highlights include:
- Ease of use: Atlas automates infrastructure tasks and provides an intuitive UI. Deploying and connecting to a cluster takes minutes.
- Performance & scale: MongoDB 8.0 delivers major performance gains (36 % faster reads and 59 % higher update throughput) and improved horizontal scaling. Automatic sharding and dynamic schemas make scaling simple.
- Integrated services: Built‑in search, vector search, stream processing and data federation allow teams to build search and AI features without integrating third‑party services. Search nodes reduce query latency by 40–60 %.
- Flexible pricing: Free, dedicated, Flex and serverless tiers suit different workloads. The Flex tier caps monthly costs at about $30 while supporting bursts up to 500 operations per second.
- Cost optimization: Enhancements released in late 2024—independent shard scaling, extended storage and more responsive auto‑scaling—give teams fine‑grained control over resources.
- AI readiness: Vector Search and the AI Applications Program reflect MongoDB’s investment in generative‑AI and machine‑learning workloads.
Frequently Asked Question
What is MongoDB Atlas?
MongoDB Atlas is a fully managed cloud database service that runs the MongoDB document database on AWS, Azure and Google Cloud. It automates deployment, patching, backups and scaling so developers can focus on building applications rather than managing servers.
Is there a free version of MongoDB Atlas?
Yes. The M0 free tier provides 512 MB of storage, shared RAM and a shared vCPU at no cost. It’s ideal for learning, prototyping or running small apps. Additional resources and features require moving to paid tiers.
What are the main pricing options?
- Dedicated clusters: Suitable for production workloads; pricing starts around $0.08/hr for an M10 cluster and scales with instance size.
- Flex tier: Designed for development or variable workloads. It costs $8 per month for up to 100 ops/sec and scales up to $30 per month for 400–500 ops/sec.
- Serverless clusters: Bill only for operations run—about $0.10 per million reads and $1 per million writes plus storage charges.
What’s new in MongoDB 8.0?
MongoDB 8.0, released in October 2024, introduces architectural changes that boost read performance by 36 % and update throughput by 59 %. It also adds range queries for Queryable Encryption, making it possible to search over encrypted data
How does Atlas support AI and vector search?
tlas includes Vector Search, a built‑in vector database for semantic search and generative‑AI workloads. In 2024 MongoDB added vector quantization to reduce storage costs and scale to billions of vectors. Dedicated search nodes provide separate infrastructure for search and vector workloads, improving query times by 40–60 %. MongoDB also launched the AI Applications Program to help customers build AI solutions.
How does Atlas manage scaling and cost optimization?
Atlas can automatically scale clusters vertically and horizontally. Recent updates introduced independent shard scaling, allowing you to scale only the shards that experience high traffic. Extended storage and 5× faster auto‑scaling further help match resources to demand while minimizing costs
Does Atlas provide tools for data visualization?
Yes. Atlas includes Data Explorer for browsing and editing documents directly in the console. It also integrates with MongoDB Compass (a GUI), Atlas Charts for creating dashboards and BI connectors for connecting to SQL‑based analytics tools. These tools make it easier to explore your data, build aggregations and generate visual insights.
Can I deploy Atlas in multiple regions?
Absolutely. Atlas supports multi‑region clusters, enabling low‑latency access for global applications and built‑in failover across regions. You choose regions during cluster creation and can add or remove regions later. Multi‑region clusters are useful for disaster recovery and compliance.