Elasticsearch is a distributed, open-source search and analytics engine built on Apache Lucene. It stores data as JSON documents and uses inverted indices to deliver near-instant full-text search across massive datasets. Elasticsearch is the core component of the Elastic Stack (ELK) and is used by companies like Netflix, eBay, and Walmart for application search, log analytics, security monitoring, and business intelligence. In 2026, Elasticsearch also supports vector search and LLM integration for AI-powered retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) pipelines.
TL;DR
- Elasticsearch is a distributed, open-source search and analytics engine built on Apache Lucene.
- It stores data as JSON documents and uses inverted indices for lightning-fast full-text search.
- Commonly used for app/website search, log analysis, business intelligence, and security analytics.
- Core component of the ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) with additional support from Beats.
- Powers real-time analytics across massive datasets using a scalable, distributed architecture.
- In 2026, it’s integrated with AI and LLMs to support intelligent search and RAG pipelines.
- Tools like Knowi offer native Elasticsearch integration, no ETL needed, plus AI-powered dashboards and multi-index joins.
- Ideal for embedding analytics into SaaS apps, monitoring infrastructure, or querying unstructured data.
- Trusted by enterprises like Netflix, eBay, and Walmart for mission-critical use cases.
- Elasticsearch continues to be a go-to solution for flexible, high-performance search and analytics.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Elasticsearch?
- How does Elasticsearch work – Elasticsearch Architecture Explained
- The Elastic Stack (ELK)
- Elasticsearch Installation Tutorial
- What is Elasticsearch used for?
- Elasticsearch vs Alternatives 2026
- Why Is Elasticsearch Popular?
- Elasticsearch in 2026: Trends to Watch
- Final Thoughts
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
When people ask, “what is Elasticsearch?”, some may answer that it’s “an index”, “a search engine”, an “analytics database”, “a big data solution”, that “it’s fast and scalable”, or that “it’s kind of like Google”. Depending on your level of familiarity with this technology, these answers may either bring you closer to an ah-ha moment or further confuse you. But the truth is, all of these answers are correct and that’s part of the appeal of Elasticsearch. Over the years, Elasticsearch and the ecosystem of components that’s grown around it called the “Elastic Stack” has been used for a growing number of use cases, from simple search on a website or document, collecting and analyzing log data, to a business intelligence tool for data analysis and visualization. So how did a simple search engine created by Elastic co-founder Shay Bannon for his wife’s cooking recipes grow to become today’s most popular enterprise search engine and one of the 10 most popular DBMS? We’ll answer that in this post by understanding what Elasticsearch is, how it works, and how it’s used. Let’s dive in.
Looking to join, blend, analyze and visualize your Elasticsearch data?
If you are trying to join and blend your elasticsearch data with SQL, APIs or cloud data, download our guide on how to integrate ELasticsearch data with any data source.
If you have a project and are trying to visualize your Elasticsearch data, take a look at our Elasticsearch Analytics page. You can also set up a 15 minute call with a member of our team to see if Knowi may be a good BI solution for your project.
What is Elasticsearch?
At its core, you can think of Elasticsearch as a server that can process JSON requests and give you back JSON data.Elasticsearch is a distributed, open-source search and analytics engine built on Apache Lucene and developed in Java. It started as a scalable version of the Lucene open-source search framework then added the ability to horizontally scale Lucene indices. Elasticsearch allows you to store, search, and analyze huge volumes of data quickly and in near real-time and give back answers in milliseconds. For teams evaluating alternatives, see our comparison of analytics tools for OpenSearch. It’s able to achieve fast search responses because instead of searching the text directly, it searches an index. It uses a structure based on documents instead of tables and schemas and comes with extensive REST APIs for storing and searching the data. At its core, you can think of Elasticsearch as a server that can process JSON requests and give you back JSON data.
How does Elasticsearch work – Elasticsearch Architecture Explained
Elasticsearch organizes data into documents (in JSON), grouped into indices (like databases). It uses an inverted index, a structure that maps words to document locations, for fast searches.
It follows a simple yet powerful process to deliver lightning-fast search results:
Document Ingestion
When you add data to Elasticsearch, it converts your content into JSON documents. Each document gets a unique ID and is assigned to an index.
Text Analysis
Elasticsearch breaks down your text using analyzers – splitting sentences into individual terms, removing common words (“the,” “and”), and standardizing formats.
Inverted Index Creation
Instead of searching documents directly, Elasticsearch creates an inverted index – a lookup table that maps every term to the documents containing it. This is why searches are so fast.
Distributed Storage
Your data gets split across multiple shards (pieces) and distributed across cluster nodes, ensuring both speed and reliability.
Query Processing
When you search, Elasticsearch quickly checks the inverted index, finds matching documents, scores them for relevance, and returns ranked results.
This architecture allows Elasticsearch to search millions of documents in milliseconds.
Logical Concepts
Documents
Documents are the basic unit of information that can be indexed in Elasticsearch expressed in JSON, which is the global internet data interchange format. You can think of a document like a row in a relational database, representing a given entity, the thing you’re searching for. In Elasticsearch, a document can be more than just text, it can be any structured data encoded in JSON. That data can be things like numbers, strings, and dates. Each document has a unique ID and a given data type, which describes what kind of entity the document is. For example, a document can represent an encyclopedia article or log entries from a web server.
Indices
An index is a collection of documents that have similar characteristics. An index is the highest level entity that you can query against in Elasticsearch. You can think of the index as being similar to a database in a relational database schema. Any documents in an index are typically logically related. In the context of an e-commerce website, for example, you can have an index for Customers, one for Products, one for Orders, and so on. An index is identified by a name that is used to refer to the index while performing indexing, search, update, and delete operations against the documents in it.
Inverted Index
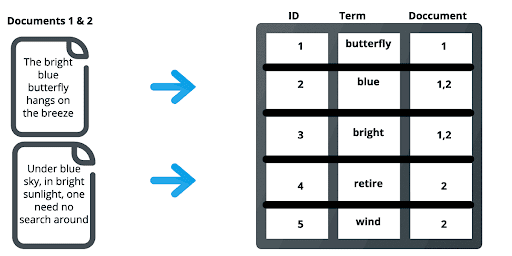
An index in Elasticsearch is actually what’s called an inverted index, which is the mechanism by which all search engines work. It is a data structure that stores a mapping from content, such as words or numbers, to its locations in a document or a set of documents. Basically, it is a hashmap-like data structure that directs you from a word to a document. An inverted index doesn’t store strings directly and instead splits each document up to individual search terms (i.e. each word) then maps each search term to the documents those search terms occur within. For example, in the image below, the term “best” occurs in document 2, so it is mapped to that document. This serves as a quick look-up of where to find search terms in a given document. By using distributed inverted indices, Elasticsearch quickly finds the best matches for full-text searches from even very large data sets.
Backend Components
Cluster
An Elasticsearch cluster is a group of one or more node instances that are connected together. The power of an Elasticsearch cluster lies in the distribution of tasks, searching, and indexing, across all the nodes in the cluster.
Node
A node is a single server that is a part of a cluster. A node stores data and participates in the cluster’s indexing and search capabilities.
An Elasticsearch node can be configured in different ways:
Master Node – Controls the Elasticsearch cluster and is responsible for all cluster-wide operations like creating/deleting an index and adding/removing nodes.
Data Node – Stores data and executes data-related operations such as search and aggregation.
Client Node – Forwards cluster requests to the master node and data-related requests to data nodes.
Shards
Elasticsearch provides the ability to subdivide the index into multiple pieces called shards. Each shard is in itself a fully-functional and independent “index” that can be hosted on any node within a cluster. By distributing the documents in an index across multiple shards, and distributing those shards across multiple nodes, Elasticsearch can ensure redundancy, which both protects against hardware failures and increases query capacity as nodes are added to a cluster.
Replicas
Elasticsearch allows you to make one or more copies of your index’s shards which are called “replica shards” or just “replicas”. Basically, a replica shard is a copy of a primary shard. Each document in an index belongs to one primary shard. Replicas provide redundant copies of your data to protect against hardware failure and increase capacity to serve read requests like searching or retrieving a document.
The Elastic Stack (ELK)
An introduction of Elasticsearch cannot be complete without touching upon Elastic Stack.
What is Elastic stack (Formerly ELK Stack)?
Elasticsearch is the central component of the Elastic Stack, a set of open-source tools for data ingestion, enrichment, storage, analysis, and visualization. It is commonly referred to as the “ELK” stack after its components Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana and now also includes Beats. Although a search engine at its core, users started using Elasticsearch for log data and wanted a way to easily ingest and visualize that data.
What is are the ELK Stack components?
Kibana
Kibana is a data visualization and management tool for Elasticsearch that provides real-time histograms, line graphs, pie charts, and maps. It lets you visualize your Elasticsearch data and navigate the Elastic Stack. You can select the way you give shape to your data by starting with one question to find out where the interactive visualization will lead you. For example, since Kibana is often used for log analysis, it allows you to answer questions about where your web hits are coming from, your distribution URLs, and so on.
If you’re not building your own application on top of Elasticsearch, Kibana is a great way to search and visualize your index with a powerful and flexible UI. However, a major drawback is that every visualization can only work against a single index/index pattern. So if you have indices with strictly different data, you’ll have to create separate visualizations for each.
For more advanced use cases, Knowi is a good option. It allows you to join your Elasticsearch data across multiple indexes and blend it with other SQL/NoSQL/REST-API data sources, then create visualizations from it in a business-user friendly UI.
For a deeper comparison of visualization tools, see our guide on Grafana vs Kibana or explore our full Kibana tutorial.
Confused about which is the best analytics tool for Elasticsearch? Read our blog comparing the top analytics tools for Elasticsearch: Kibana vs Grafana vs Knowi
Logstash
Logstash is used to aggregate and process data and send it to Elasticsearch. It is an open-source, server-side data processing pipeline that ingests data from a multitude of sources simultaneously, transforms it, and then sends it to collect. It also transforms and prepares data regardless of format by identifying named fields to build structure, and transform them to converge on a common format. For example, since data is often scattered across different systems in various formats, Logstash allows you to tie different systems together like web servers, databases, Amazon services, etc. and publish data to wherever it needs to go in a continuous streaming fashion.
Beats
Beats is a collection of lightweight, single-purpose data shipping agents used to send data from hundreds or thousands of machines and systems to Logstash or Elasticsearch. Beats are great for gathering data as they can sit on your servers, with your containers, or deploy as functions then centralize data in Elasticsearch. For example, Filebeat can sit on your server, monitor log files as they come in, parses them, and import into Elasticsearch in near-real-time.
Elasticsearch Installation Tutorial
Quick Start with Docker )
1. Install Docker
Download Docker Desktop for your operating system.
2. Run Elasticsearch
docker run -d --name elasticsearch
-p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300
-e "discovery.type=single-node"
-e "xpack.security.enabled=false"
elasticsearch:8.11.0
3. Verify Installation
Open http://localhost:9200 in your browser. You should see JSON response with cluster information.
4. Add Sample Data
curl -X POST "localhost:9200/products/_doc/1"
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"name": "Laptop",
"price": 999,
"category": "Electronics"
}'
5. Search Your Data
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/products/_search?q=laptop"
What is Elasticsearch used for?
Now that we have a general understanding of what Elasticsearch is, the logical concepts behind it, and its architecture, we have a better sense of why and how it can be used for a variety of use cases. Below, we’ll examine some of Elasticsearch’s primary use cases and provide examples of how companies are using it today.
Primary Use Cases of Elasticsearch
Application search
For applications that rely heavily on a search platform for the access, retrieval, and reporting of data.
Website search
Websites which store a lot of content find Elasticsearch a very useful tool for effective and accurate searches. It’s no surprise that Elasticsearch is steadily gaining ground in the site search domain sphere.
Enterprise search
Elasticsearch allows enterprise-wide search that includes document search, E-commerce product search, blog search, people search, and any form of search you can think of. In fact, it has steadily penetrated and replaced the search solutions of most of the popular websites we use on a daily basis. From a more enterprise-specific perspective, Elasticsearch is used to great success in company intranets.
Logging and log analytics
As we’ve discussed, Elasticsearch is commonly used for ingesting and analyzing log data in near-real-time and in a scalable manner. It also provides important operational insights on log metrics to drive actions.
Infrastructure metrics and container monitoring
Many companies use the ELK stack to analyze various metrics. This may involve gathering data across several performance parameters that vary by use case.
Security analytics
Another major analytics application of Elasticsearch is security analysis. Access logs and similar logs concerning system security can be analyzed with the ELK stack, providing a more complete picture of what’s going on across your systems in real-time.
Business analytics
Many of the built-in features available within the ELK Stack makes it a good option as a business analytics tool. However, there is a steep learning curve for implementing this product and in most organizations. This is especially true in cases where companies have multiple data sources besides Elasticsearch–since Kibana only works with Elasticsearch data. A good alternative is Knowi, which offers Elasticsearch analytics for business users, an analytics platform that natively integrates with Elasticsearch and allows even non-technical business users to create visualizations and perform analytics on Elasticsearch data without prior knowledge or expertise of the ELK Stack.
How are companies using Elasticsearch?
Elasticsearch has popular use cases for log search and analytics, application monitoring, web search, application search, business analytics. There are many well-known companies and enterprises that are using Elasticsearch includin
Netflix
Netflix relies on the ELK Stack across various use cases to monitor and analyze customer service operations and security logs. For example, Elasticsearch is the underlying engine behind their messaging system. In addition, the company chose Elasticsearch for its automatic sharding and replication, flexible schema, nice extension model, and ecosystem with many plugins. Netflix has steadily increased their use of Elasticsearch from a few isolated deployments to over a dozen clusters consisting of several hundred nodes.
Ebay
With countless business-critical text search and analytics use cases that utilize Elasticsearch as the backbone, eBay has created a custom ‘Elasticsearch-as-a-Service’ platform to allow easy Elasticsearch cluster provisioning on their internal OpenStack-based cloud platform.
Walmart
Walmart utilizes the Elastic Stack to reveal the hidden potential of its data to gain insights about customer purchasing patterns, track store performance metrics, and holiday analytics — all in near real-time. It also leverages ELK’s security features for security with SSO, alerting for anomaly detection, and monitoring for DevOps
Elasticsearch vs Alternatives 2026
Elasticsearch vs OpenSearch
For a detailed comparison, read our full guide: Elasticsearch vs OpenSearch: Which One to Choose?
Elasticsearch Advantages:
- Better commercial support and documentation
- Advanced ML features and anomaly detection
- Stronger enterprise security features
OpenSearch Advantages:
- Fully open-source (no licensing restrictions)
- AWS managed service available
- Growing community adoption
Learn more: OpenSearch: The Open-Source Search Engine | OpenSearch Challenges and Use Cases
Elasticsearch vs Solr
Choose Elasticsearch if:
- You need real-time analytics, modern APIs, and easier scaling
Choose Solr if:
- You have complex search requirements and need extensive customization
Elasticsearch vs Vector Databases (2026 Trend)
While vector databases like Pinecone excel at AI similarity search, Elasticsearch now offers:
- Built-in vector search capabilities
- Hybrid search (combining text and semantic search)
- Unified platform for both traditional and AI-powered search
Why Is Elasticsearch Popular?
According to StackShare and developer communities:
- Powerful REST API
- Open source and free
- Easy to set up and scale
- Near real-time insights
- Strong community support
- Built-in analytics and distribution
Confused which datasource to use – Elasticsearch or MySQL? Read our blog comparing both these datasources: Elasticsearch vs MySQL
Elasticsearch in 2026: Trends to Watch
AI-Native Features:
- Enhanced vector search for RAG applications
- Built-in LLM integration for semantic search
- Automated anomaly detection improvements
Performance Upgrades:
- Faster indexing with new storage engines
- Improved query optimization
- Better resource management for large datasets
Developer Experience:
- Simplified APIs for common operations
- Better observability and monitoring tools
- Enhanced integration with modern data stacks
Cloud-First Approach:
- Serverless Elasticsearch options
- Edge computing optimizations
- Multi-cloud deployment strategies
Final Thoughts
Elasticsearch is at its core a search engine, whose underlying architecture and components makes it fast and scalable, sitting at the heart of an ecosystem of complementary tools that together can be used for many uses cases including search, analytics, and data processing and storage.
If you’re interested in learning more about Elasticsearch and trying it out for yourself, you can get started here. And for more advanced use cases in which you need to join and blend your Elasticsearch data across multiple indexes and other SQL/NoSQL/REST-API data sources, check out our guid on integrating Elasticsearch with other datasources. Happy searching!
Related Elasticsearch guides:
- Elasticsearch Aggregations Guide
- How to Join Elasticsearch with Other Data Sources
- Building Elasticsearch Queries with Knowi
- ES|QL Lookup Join Limitations
- Kibana Embedding Limitations
Ready to see Elasticsearch analytics in action? Book a demo with Knowi to explore native Elasticsearch integration with AI-powered dashboards.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Elasticsearch used for?
Elasticsearch is used for full-text search, log and event data analysis, infrastructure monitoring, security analytics, and business intelligence. It supports real-time analytics across massive datasets.
What is Elasticsearch used for?
Elasticsearch is used for full-text search, log and event data analysis, infrastructure monitoring, security analytics, and business intelligence. It supports real-time analytics across massive datasets.
Can I use Elasticsearch with AI tools?
Yes, in 2026 Elasticsearch is commonly used alongside AI and LLMs to build intelligent search assistants and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipelines.
What are some alternatives to Kibana for visualizing Elasticsearch data?
Knowi is a powerful alternative to Kibana that supports multi-index joins, AI-generated dashboards, and analytics across NoSQL, SQL, and REST data sources without ETL.
How does Elasticsearch differ from traditional databases?
Elasticsearch uses an inverted index for fast search, stores data in JSON documents, and supports distributed real-time analytics, unlike traditional relational databases that use tables and SQL for queries.
What is the ELK Stack and how does it relate to Elasticsearch?
The ELK Stack consists of three open-source tools: Elasticsearch (search and analytics engine), Logstash (data ingestion and processing pipeline), and Kibana (data visualization dashboard). Together with Beats (lightweight data shippers), they form the Elastic Stack. Elasticsearch serves as the core storage and search layer, while Logstash handles data collection and transformation, and Kibana provides visualization capabilities. The ELK Stack is widely used for log analysis, infrastructure monitoring, and security analytics.
How does Elasticsearch compare to OpenSearch in 2026?
Both Elasticsearch and OpenSearch are built on Apache Lucene, but they differ in licensing and features. Elasticsearch offers better commercial support, advanced ML features, and stronger enterprise security under the Elastic License. OpenSearch is fully open-source (Apache 2.0 license) with AWS managed service support and a growing community. Choose Elasticsearch for enterprise features and support, or OpenSearch for fully open-source deployments and AWS integration.